By: Sakias Moro
@2023
July, 23
Bitcoin mining and bitcoin staking
Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and added to the circulating supply. It also serves as the mechanism to validate and secure transactions on the Bitcoin network. Mining involves solving complex mathematical problems, and the participants in this process are called miners. Here’s how it works:
1.Proof-of-Work ( POS) Consensus: Bitcoin uses a consensus algorithm called Proof-of-Work. Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle, which requires significant computational power. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees.
2. Mining Hardware: Miners use specialized computer hardware, known as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) or Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), to perform the intensive computations required for mining. These machines are designed to maximize mining efficiency and hash rate.
3. Mining Pools: Due to the competitive nature of mining and the increasing difficulty of the puzzles, individual miners often join mining pools. In a mining pool, miners combine their computing power, and when any member of the pool successfully mines a block, the rewards are distributed among all participants according to their contributed hash power.
4. Block Reward: As of my last observations from September 2021, the block reward for successfully mining a block on the Bitcoin network was 6.25 bitcoins. However, it’s important to note that the Bitcoin protocol is designed to halve the block reward approximately every four years. This event is known as the “halving,” and it occurs every 210,000 blocks. The most recent halving took place in May 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 bitcoins to 6.25 bitcoins.
5. Mining Difficulty: The Bitcoin network automatically adjusts the difficulty of the mining puzzle every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks) to ensure that blocks are mined, on average, every 10 minutes. If more miners join the network, the difficulty increases to maintain the 10-minute block time.
6. Energy Consumption : Bitcoin mining is an energy-intensive process because of the computational power required. This has raised concerns about its environmental impact, especially if the energy used comes from non-renewable sources.
Staking Program (Proof-of-Stake):
Staking is an alternative consensus mechanism to mining, used by various cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum’s upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. Instead of relying on proof-of-work, staking relies on proof-of-stake (PoS). In a PoS system, validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they “stake” or lock up as collateral. Here’s how staking works:
1. Proof-of-Stake Consensus: In PoS, validators are selected to propose new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to lock up as a stake. The more coins a validator stakes, the higher the chance they have of being chosen to create a block and receive rewards.
2. Staking Process: To participate in a staking program, a user needs to lock up a certain amount of the cryptocurrency in a specialized wallet or smart contract. By doing so, they become a validator and actively participate in the network’s consensus mechanism.
3. Block Validation and Reward: When a validator is chosen to create a new block, they must include valid transactions and broadcast the new block to the network. If the block is accepted, the validator is rewarded with transaction fees and newly created coins, similar to how miners are rewarded in PoW
4. Slashing: PoS introduces the concept of “slashing” to discourage malicious behavior by validators. If a validator attempts to double-spend or behaves dishonestly, a portion or all of their staked coins may be “slashed” or taken away as a penalty.
5. Energy Efficiency: PoS is often considered more energy-efficient than PoW, as it doesn’t require the same level of computational power. This is because validators are not required to solve complex mathematical puzzles, and the selection process is based on their staked coins.
6. Lock-up Period and Liquidity: One consideration for users participating in staking programs is that their staked coins are usually locked up for a certain period. This means they may not be able to access or sell those coins until the lock-up period expires, which can affect liquidity.
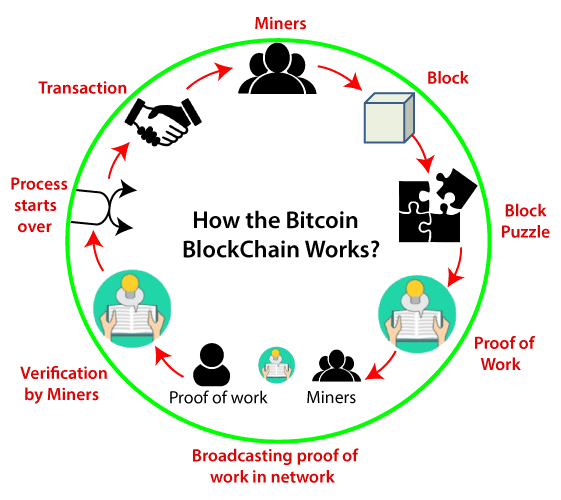
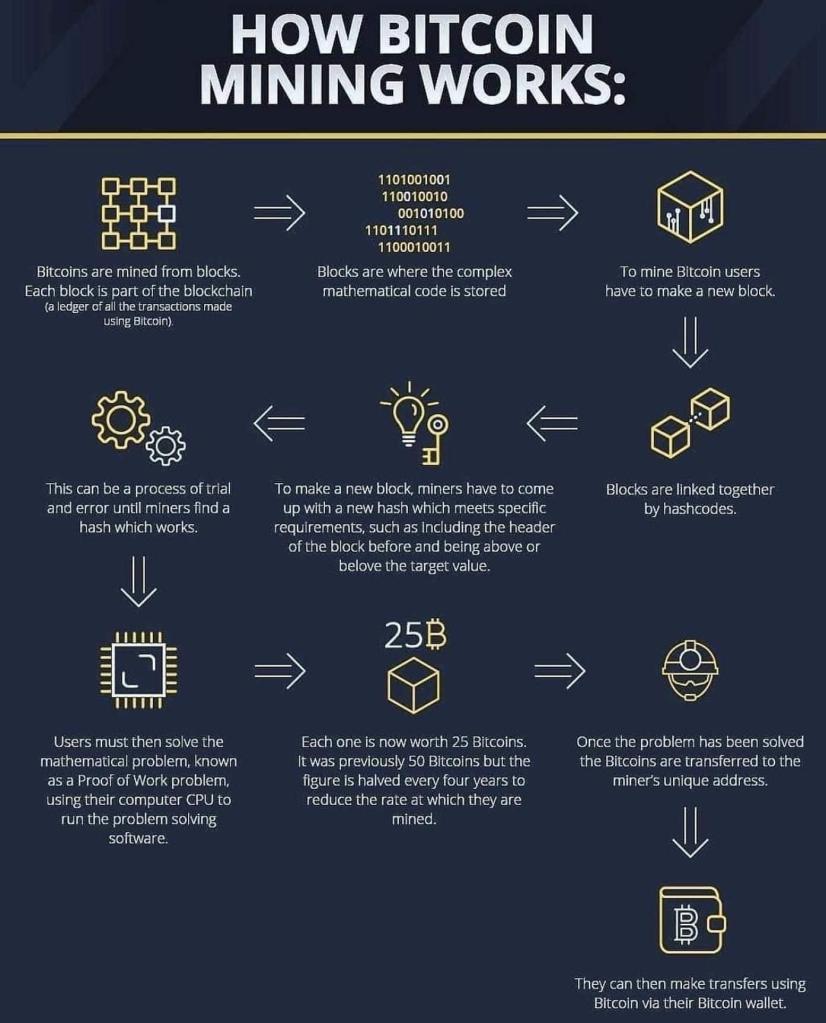
It’s worth mentioning that the details of staking programs can vary significantly between different cryptocurrencies, so it’s essential to research the specific staking mechanism of the Certain cryptocurrency Bitcoin mining and staking are integral parts of their respective blockchain networks and play crucial roles in securing and validating transactions. Mining is prevalent in the Bitcoin network, while staking gains popularity in other blockchain projects as an energy-efficient and scalable alternative.

